large cars
Driving school
theory book
for category C - D - C/E - D/E
Large cars and lorries
- 4. Electrical systems, lights, reflectors, signalling device m.v.
- Other legal provisions regarding the electrical installation:
- Checking lights:
- Checking the number plate light:
- Stop lights
- Horn
- The car's horn should have a clear, constant tone.
- Indicator lights
- Checking turn signal lights
- Side reflectors/side marker lights
- Mandatory lights on the front of the car:
- Other legal regulations on permitted lights and reflectors
- Mandatory lights on the rear of the car:
- Test your knowledge
- Cat. C - D - C/E - D/E - D/E - Section 4
Large cars - Categories C and D.
4. Electrical systems, lights, reflectors, signalling device m.v.
Your car's starter motor, lights, indicators and stop lights, horn, windscreen wipers and washers, heater fan, instruments and indicator lights, etc. are all powered by electricity.
Power is drained from one pole of the accumulator through wires, fuses and switches to the power-consuming parts and through the ground connection back to the other pole of the accumulator. The accumulator is divided into compartments (cells) containing lead plates immersed in a mixture of sulphuric acid and distilled water.
Each cell must be filled, or topped up, with distilled water so that the plates are covered.
Powder formation (sulphation) around the accumulator and its terminals must be washed away to avoid corrosion.
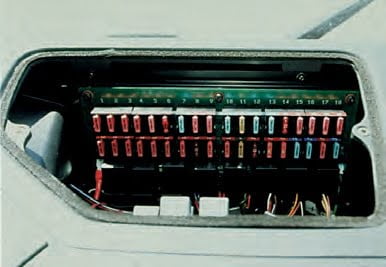
To ensure an efficient power supply, all wires, fuses and plugs must be clean, intact and well insulated, and all connections, including ground connections, must be tight and free from corrosion.
Other legal provisions regarding the electrical installation:
- The battery must be secured and positioned or covered in such a way that a short circuit cannot occur.
- The electrical system must be fitted with fuses to prevent fire in the event of a short circuit. When installing electrical accessories, an additional fuse must be installed.
- If the indicators are flashing significantly faster than usual, this is usually a sign that one or more indicators are not working.
- All lights and reflectors must be intact and clean, and all lights must be able to illuminate.
- The horn should have a clear, constant tone.
Checking lights:
You must be able to check whether the following requirements for lights are met:
- All lights and reflectors must be clean and intact.
- Paired lights must be the same colour and intensity.
- Low beams should not dazzle.
To check the range of the dipped beam without dazzling, measure up to the centre of the lamp, walk 10 metres in front of the car and check that the upper edge of the light border has dropped at least 10 cm from the measured height.
As such, the dipped beam must illuminate the road at least 30 metres ahead (it must illuminate further ahead on the right side than on the left).
- Mandatory position lamps, tail lamps, licence plate lamps and marker lamps must be capable of being switched on when the engine is stopped and must not be capable of being switched off when the main beam, dipped beam or fog lamps are switched on.
- After this check, measure 30 metres ahead of the car and see if the low beam illuminates the road sufficiently for the 30 metres ahead. (Be aware that a heavy load on the back of the car may cause the dipped beam to shine brighter and thus appear dazzling).
- All lights must be able to illuminate.
The dipped beam has dropped 10 cm below your finger at a distance of 10 metres from the headlight.
Uneven colour or brightness in a pair of lights is immediately noticeable. This may be because you are only replacing the bulb that has burned out to save money. Therefore, you should also replace the other bulb to ensure the same brightness in the pair of lights.
If replaced bulbs are not properly inserted into the socket, the dipped beam will glare. This can be checked by holding a sheet of white paper over the switched-on light. The boundary between light and dark will then be clearly visible.
Note:
Modern cars equipped with elipse lights (the small ones where the low and high beams are built into separate lamps) have a different look and different rules when it comes to controlling the low beam. (See your car's owner's manual).
Checking the number plate light:
- At least one number plate light with white light that can illuminate the rear number plate.
Mandatory reflectors and reflective panels
The rear of the vehicle must be fitted with an even number of red, approved and labelled reflectors, which must not be triangular.
Trucks must be fitted with reflective panels with diagonal red/yellow stripes at the rear. Any additional red reflectors must not be triangular and must be arranged symmetrically.
Stop lights
There must be at least two stop lamps at the rear of the vehicle, which must provide a significantly brighter red light than the rear lights and light up as soon as the brake pedal is pressed.
The stop light is checked as follows:
- The stop light is switched on by either letting a helper depress the brake pedal or by looking for the reflection of a wall or similar from inside the car.
Horn
The car's horn should have a clear, constant tone.
Indicator lights
A car must be equipped with an equal number of front, rear and side indicators.
Checking turn signal lights
- All indicators must flash an amber light that is clearly visible in sunlight, and an indicator light must flash in time with the indicator.
- A special switch must be able to switch on all indicators simultaneously so that they can act as hazard warning lights.
Side reflectors/side marker lights
Vehicles with a length exceeding 6 metres must be equipped with yellow approved and marked reflectors and yellow side marker lights distributed on the vehicle's
pages.
Side reflectors and side marker lights can be integrated.
Side marker lights must be clearly visible from a distance of 300 metres without glare.
- Older cars (before 1996) may be equipped with either side reflectors or side marker lights.
Checking reflexes:
- Reflectors must be intact and clean.
Legal regulations on mandatory lights
A car may only be equipped with mandatory and authorised lights and reflectors.
Mandatory lights on the front of the car:
- Two white or amber high beam headlights that can illuminate the road at least 100 metres in front of the car and are connected to an indicator light at the driver's seat.
- Two lamps with white or amber asymmetric low beam that must illuminate the road at least 30 metres in front of the car without dazzling.
- Two headlights with position lights that are clearly visible for at least 300 metres in front of the car.
- Two forward-facing marker lights if the vehicle is wider than 2.10 m. The lights must be white and clearly visible from at least 300 metres away
without glare.
(The car in the picture is without marker lights due to lack of width).
- High beams can be fitted with overtaking lights.
- Buses with a gross vehicle weight of more than 3.5 tonnes may be fitted with advertising or distinguishing signs above the windscreen.
Other legal regulations on permitted lights and reflectors
Permitted lights and reflectors include:
Additional high beam headlights, daytime running lights, additional rear lights, additional turn signal lights, additional stop lights. Front fog lamps, reversing lamps, rear fog lamps, search and work lamps, marker lamps, parking lamps and overtaking lamps, for which special rules apply. In addition, the vehicle may be equipped with white reflectors at the front, yellow reflectors on the sides and additional red reflectors at the rear.
Trucks can be equipped on the sides with reflective contour markings in yellow or white and advertising or logos in a low-reflective material that can be in any colour. Trucks can also be equipped with red contour markings on the rear.
Mandatory lights on the rear of the car:
- At least two rear lights with red light that can be clearly seen from at least 300 metres behind the vehicle.
- At least one number plate light with white light that can illuminate the number plate so that it can be read clearly from a distance of at least 20 metres.
- Two stoplights.
- Two rear marker lights if the car is wider than 2.10 m. The lights must have a red light that is clearly visible from a distance of at least 300 metres without dazzling. (The car in the picture is without marker lights due to lack of width).
Test your knowledge
Cat. C - D - C/E - D/E - D/E - Section 4
Select the questions you think are the right ones.