large cars
Driving school
theory book
for category C - D - C/E - D/E
Large cars and lorries
- 2. Brakeman
- Trailer brakes
- Hose couplings
- Control valves
- Brake valves
- Compressed air tank
- Brake circuit parts
- Changeover valve (Ranger valve)
- Brake diaphragms
- All types of braking systems can be built as ABS brakes
- Additional brakes
- Checking the trailer supply circuit
- Checking the trailer's steering circuit
- Checking the service brake is sufficiently effective
- Signs of brake failure
- Other legal provisions on brakes
- Test your knowledge
- Cat. C - D - C/E - D/E - Trailers - Section 2
2. Brakeman
Trailer brakes
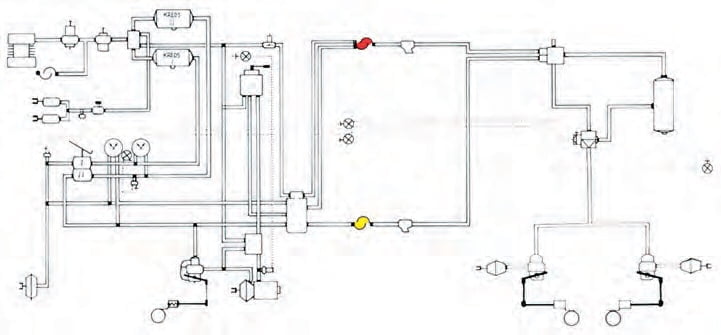
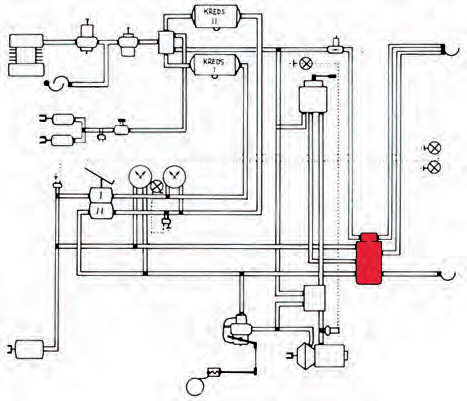
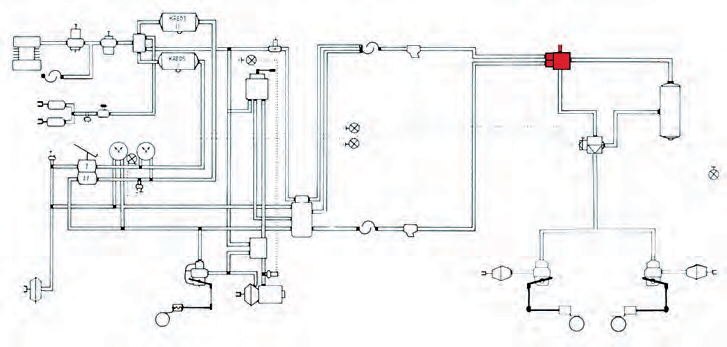
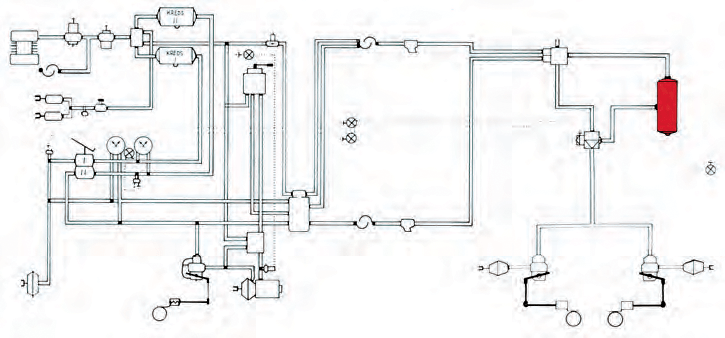
Service brakes on trailers with a maximum authorised weight of over 3500 kg are usually compressed air mechanical brakes.
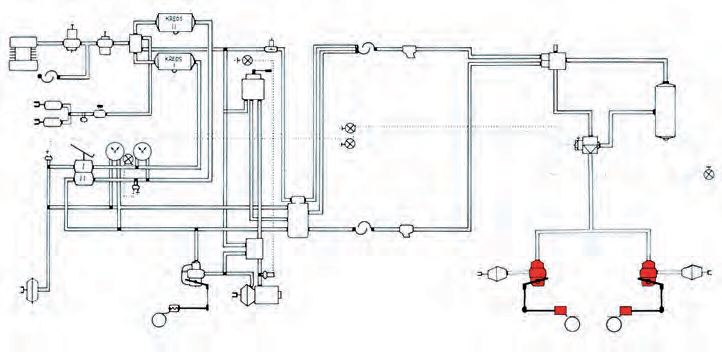
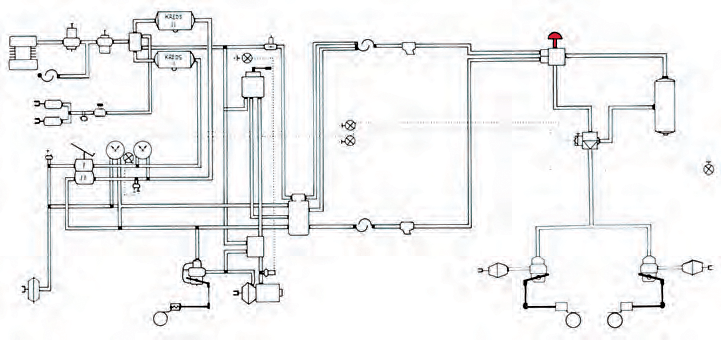
Two-wire braking system
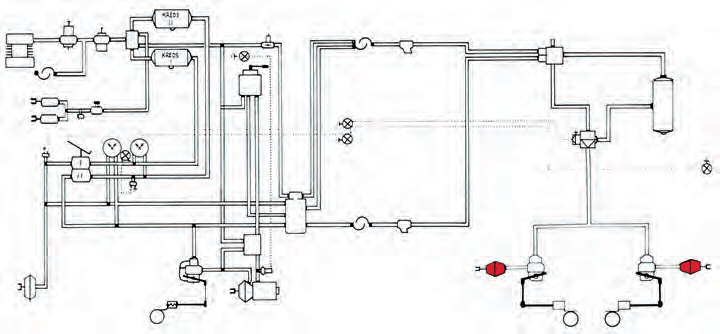
The braking system consists of:
- The supply circle.
- The steering circle.
- The brake circuit.
A two-wire braking system has two hose connections, a supply hose and a control hose between the vehicle and the trailer.
Through the supply hose, the vehicle's air reservoir is supplied with compressed air for braking.
Through the control hose, the trailer's brake pressure is controlled by regulating the pressure in the hose (compressed air signal). Both hoses are flexible high-pressure hoses.
Tube filters can be installed in connection to the hoses to collect impurities.
Hose couplings
The hoses are connected to the car through hose couplings that consist of two halves, one placed on the car and the other on the hose. The supply hose coupling may be marked in red colour and the control hose coupling in yellow colour. The hose couplings for the supply circuit and the control circuit can be combined into one coupling (Duo-matic).
Duo-matic.
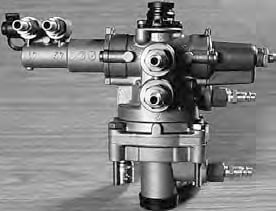
Control valves
The control valve located on the car has two functions:
- To allow the passage of air pressure from the vehicle's supply circuit to the trailer's compressed air tank.
- To direct compressed air from the car's brake circuit to the trailer's brake valve when the car is braked. The strength of the signal depends on the car's brake pressure.
Brake valves
The brake valve located on the trailer has two functions:
- To direct the compressed air from the vehicle's supply circuit to the trailer's compressed air tank.
- To regulate the air pressure in the trailer brake circuit and thus the braking force in relation to the air pressure signal from the car brake circuit.
Compressed air tank
The trailer's compressed air tank stores the compressed air and must be drained of condensation, possibly automatically.
Brake circuit parts
Brake regulator (ALB regulator)
The ALB controller automatically adapts the braking force to the trailer load. The ALB controller is usually mounted on the vehicle's chassis frame and is in mechanical connection with the wheel axle.
ALB with air suspension
On cars with air suspension, where the distance between the chassis frame and the axle is the same regardless of the load, the brake force regulator is controlled by the pressure in the air bellows.
The air pressure in the air bellows increases with increased load. When the bellows pressure changes, the regulating pressure at the air-controlled ALB valve, which regulates the compressed air to the brake diaphragms, also changes.
If the braking system is designed as ABS, in some cases there will be no brake controller. If ABS does not work, it is illegal to continue driving.
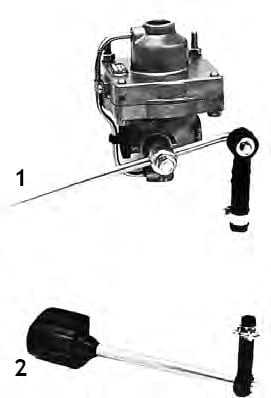
Changeover valve (Ranger valve)
The changeover valve is required on trailer vehicles.
When switched on, the switching valve automatically moves to the operating position. Always remember to check this as a precautionary measure.
When disconnecting, the trailer vehicle is braked due to the pressure drop in the hose connection to the car.
To manoeuvre the uncoupled trailer, the button on the switching valve must be pulled out, releasing the trailer brakes. When the button is
is pressed, the trailer is braked again.
This manoeuvre can be repeated as long as there is enough pressure in the tank to brake the trailer.
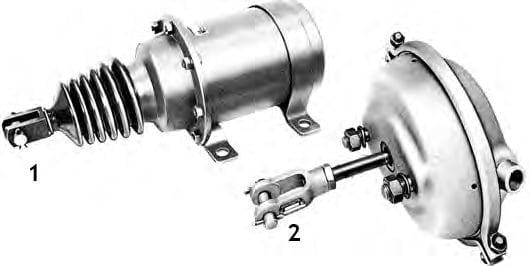
Brake diaphragms
Brake diaphragms, located near the wheels, are responsible for converting the energy of compressed air into motion to affect the wheel brakes. (Some older trailers may be equipped with brake cylinders instead of brake diaphragms). The wheel brake can be a drum brake or a disc brake.
- The brake diaphragm travel must not exceed a quarter of the diaphragm housing clamping band diameter.
Pipes and hoses connect the individual parts in the different circuits.
1. Piston cylinder.
2. Membrane cylinder.
All types of braking systems can be built as ABS brakes
The ABS system is designed in such a way that sensors are placed at each wheel to detect the rotation of the wheel by means of a toothed rim. The sensors send signals about the rotation of each wheel to an electronic control box. If one or more wheels tend to lock when braking, the electronic control box will regulate the pressure to the wheel brakes to prevent the wheels from locking. The ABS braking system is designed to allow steering and braking simultaneously to a certain extent. When braking with a vehicle combination with ABS brakes, the ABS braking system ensures that the wheels are kept in rotation and do not lock. When the ABS braking system regulates, some smaller lorries may experience vibrations in the brake pedal. This is normal and means that the system is working. Regardless of the vibrations, the pressure on the brake pedal should be maintained as long as braking is desired. If the ABS braking system is not working, the braking characteristics will change and only driving to the nearest workshop is permitted.
Additional brakes
Trailers can be equipped with the following brakes:
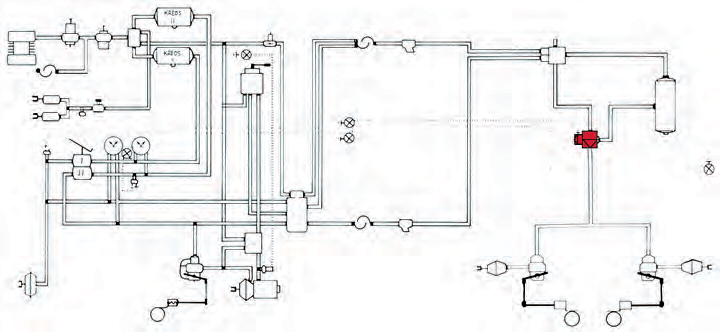
Auxiliary brake. The valve shown in the picture is a solenoid valve. When the vehicle's engine brake or retarder is activated, a current pulse is passed through the trailer's electrical cable, activating the valve to open compressed air for partial braking of the trailer.
Reverse brake. A system that automatically brakes using the trailer brakes when the vehicle is put in reverse and a sensing strip at the rear of the trailer is touched.
Checking the trailer supply circuit
Compressed air tanks
- Compressed air tanks must be securely fastened and not visibly tarnished or dented.
Pipes and hoses
- Pipes and hoses must be tight and free of corrosion, cracks or leaks, as judged at readily accessible locations.
Hose couplings
- Must be tight, judged by audible air leakage, and correctly coupled. (Often equipped with a lock from which an "engagement" is felt between the 2 coupling parts).
Checking the trailer's steering circuit
Control valve and brake valve
- The control valve (located on the car) and the brake valve (located on the trailer) are checked by activating the brake pedal and then releasing it. You will then hear the brake diaphragms or brake cylinders bleeding (audible leakage of air).
- Hose connections, pipes and hoses are checked as on the supply circuit.
Checking the trailer brake circuit
Mechanical brake force regulator (ALB valve)
The ALB controller should automatically regulate the braking force according to the trailer load.
- The mechanical connections of the ALB controller must be intact so that the valve arm can move freely. When the valve arm moves, the air pressure in the brake circuit must change, this may be audible as a leakage of air.
Pipes and hoses
- Check as on the supply circuit.
Air consumption
- As a general rule, air consumption during full braking should not exceed 0.5 bar, as this may indicate a lack of brake adjustment on either the car or the trailer.
Checking the service brake is sufficiently effective
With the supply hose disconnected between the vehicle and trailer, try to tow the trailer. If this is not possible, or only with great difficulty, the braking performance is considered sufficient.
- The service brake on newer road trains must have an effect such that the braking distance at 30 km/h does not exceed approximately 10 metres.
Signs of brake failure
- Excessive inflation time can be a sign of leaks in the brake system, possibly at hose couplings.
- Distortion during braking or uneven braking indicates moisture or dirt on brake linings or defective wheel brakes, brake diaphragms or cylinders.
- Uneven braking or sudden chopping from one or more wheels indicates a fault in the brake drums/brake discs or brake lining.
- Reduced braking performance indicates a lack of brake adjustment or incorrectly adjusted, possibly defective, ALB valve.
- Delayed braking action or excessive air consumption (generally no more than 0.5 bar) can indicate too long piston travel in compressed air diaphragms or cylinders (misalignment).
- Wheel lock-up during moderate braking can be a sign of an incorrectly adjusted, possibly defective ALB valve.
- Reduced braking effect after coupling the trailer may indicate insufficient braking performance of the trailer ("pushing" the lorry). The braking performance of the trailer may also be insufficient, even if the trailer combination as a whole fulfils the recommended braking distances.
- If the indicator light for the ABS braking system does not go out within a short time after starting, this indicates a fault in the ABS braking system and continued driving is illegal (only driving to the workshop is legal).
Other legal provisions on brakes
- The trailer must be equipped with a service brake and parking brake.
- Newer trailers must be equipped with ABS brakes.
- The service brake must be connected to the service brake of the towing vehicle.
- The service brake, which must act on all wheels, must be able to brake and stop the trailer safely, quickly and effectively at any speed and under all load conditions.
- - The trailer has no emergency brake, but it is a requirement that the service brake is designed so that the trailer brakes automatically in the event of a break in the coupling device between car and trailer.
- The vehicle's emergency brake must be able to activate the trailer's service brake.
- On vehicles without a pressure gauge on the vehicle, the compressor must be able to fill the vehicle's empty air tanks in less than 6 minutes until the control light on the vehicle switches off or the alarm is deactivated.
- On systems with pressure gauges, 2/3 of the working pressure must be reached in less than 6 minutes.
Parking brake
Trailers must be equipped with a parking brake that works by transmitting a pull on the handbrake lever through rods or cables to the wheel brake on one or more axles.
Control:
- The control handle must be easy to operate.
- Wires and similar must be undamaged and the mechanical parts must not be able to move to the bottom position.
- It must be possible to hold the parking brake in the activated position.
Test your knowledge
Cat. C - D - C/E - D/E - Trailers - Section 2
Select the questions you think are the right ones.