Passenger car
Driving school
theory book
to category B
Sections 6.1 - 6.2: Basic rules for driving - What traffic laws say
Directions for travelling
Directions are traffic signals, traffic signs, lane stripes, police signs and the general rules of the road.
Validity of the Road Traffic Act
The Road Traffic Act on driving applies in all public and private places where there is general traffic.
Cars are usually only allowed to drive on the part of the road designated for cars, motorbikes and large mopeds.
Driving instructions
You must obey the driving instructions given by traffic signals, traffic signs, lane markings, etc. If traffic is regulated by the police, you must comply with their instructions, even if traffic signals, traffic signs and lane markings say otherwise, or if it contradicts an otherwise applicable traffic rule.
Instructions can also be given by others who are entitled to do so, such as the Home Guard, the armed forces, rescue services and civil defence in special situations.
You must be familiar with police instructions and road signs as well as these signs:
Traffic signs may be indicated on orientation signs.
Safe and unhindered traffic flow
You need to know the basic rules of the Road Traffic Act and how to show consideration for certain road users. This includes understanding the meaning of the terms "danger", "inconvenience" and "unnecessary inconvenience".
Basic rules
When travelling in traffic, you must always show consideration and exercise due care so that you do not cause danger or inconvenience to others or damage to anyone, but also so that traffic is not unnecessarily impeded or disrupted. You must also show consideration for those who live or spend time by the road. And when you encounter children, school patrols, elderly or disabled people, you must be especially careful and considerate.
During periods when the temperature is around freezing, pay special attention to your speed when driving where there are damp areas along the road, at embankments and on bridges. Also, pay special attention to your speed when travelling on roads where tractor traffic is frequent during certain periods, causing road pollution.
And finally, you need to drive at a suitably low speed.
When performing certain manoeuvres, you may not always be able to avoid getting in the way of others, so you need to make sure that you don't cause "unnecessary inconvenience". This could be, for example, when starting off from the side of the road, changing lanes or if you need to brake very suddenly.
Before you reverse
- Make sure it can be done without danger or inconvenience to others.
Drawing
Before starting from the edge of the carriageway, turning and before turning, signal with turn signals. Always signal before changing lanes on motorways. The same applies to any other significant change in the vehicle's position to the side, including when entering and exiting a motorway. On other roads, you must signal when necessary to guide other traffic. When stopping or quickly reducing speed, give a signal with a stop light. Signs must be given well in advance of the intended manoeuvre in a clearly visible and unambiguous manner. All signalling must cease when a manoeuvre is completed.
Signalling and use of lights outside of the headlight switch-on time
If it is necessary to warn others of a hazard, you must do so by flashing your headlights or by giving a short signal with the horn. Any other use of the horn is illegal. Outside of the headlight switch-on time, you must use dipped headlights. Instead of dipped headlights, you can use special daytime running lights or fog lights.
Free passage for certain road users
You must hold back or give way to groups of children under the supervision of a leader, defence and emergency services columns, funeral processions and other closed parades. Keep the road open well in advance for emergency vehicles. And if necessary, pull over and stop. Never drive so close to the scene of an accident that you obstruct the rescue work.
People and goods etc.
Valley
A car must not be wider than 2.55 metres, longer than 12 metres and taller than 4 metres with or without a load. With persons, luggage or other items, the weight must not exceed the maximum authorised gross weight stated in the vehicle's registration certificate.
Passengers
Passengers and cargo must be positioned so that you have a clear view and enough space to steer the vehicle without difficulty. There must not be so many passengers in the vehicle that they could endanger themselves or others. Therefore, they must also be seated safely individually and use a seat belt when one is available. The seat belt can be used with a booster cushion. The adjustment of the headrest must be customised for each individual user.
Children's
- Instead of wearing a seat belt, 3-6 year olds can use a child seat or other approved safety equipment adapted to the child's height and weight.
- Children under the age of 3 and under 135 cm must use a child seat or other approved safety equipment adapted to the child's height and weight instead of a seat belt. However, this does not apply if they are placed in the rear seat and the rear seats are not equipped with seat belts. It also does not apply if they are placed in the rear seat and the rear seat seating positions with seat belts are occupied by other children under 3 years of age with adapted safety equipment. Children under 3 years of age must use a seat equipped with a seat belt (in combination with customised safety equipment) in preference to others.
- No more passengers may be carried than there are seats with seat belts.
- It is your responsibility to ensure that passengers under the age of 15 use seat belts or other safety equipment.
Gods
- Goods must be placed so that they do not obscure indicators, lights and licence plates, and so that they do not make unnecessary noise, drag or fall onto the road, or otherwise obstruct or endanger traffic.
- If the transport of goods or luggage in the back of the vehicle covers one or more mandatory lights and reflectors, a light bar must be placed on the back of the goods/baggage.
- Goods that protrude more than 1 metre beyond the front or rear of the vehicle, or more than 15 cm beyond the sides, must be marked with a cloth or in another clear manner. For commercial transport, the goods must be marked with a white cylinder that is 30 cm high, 10 cm in diameter and has two red reflective strips.
- During headlight switch-on time, protruding goods must be marked with this cylinder as well as a red light to the rear and a white light to the front, regardless of whether the transport is private or commercial.
- If you drop or spill something on the road that poses a risk to traffic, it must be removed immediately. If this is not possible, you must use signage or similar to warn others of the risk.
- You may not tow a sledge, trolley or similar behind a car, nor may you pull a person on skis, skates, roller skates or similar.
- A maximum of one trailer may be attached to a car and only if the car is authorised to do so.
- The transport of dangerous goods must be carried out according to special rules.
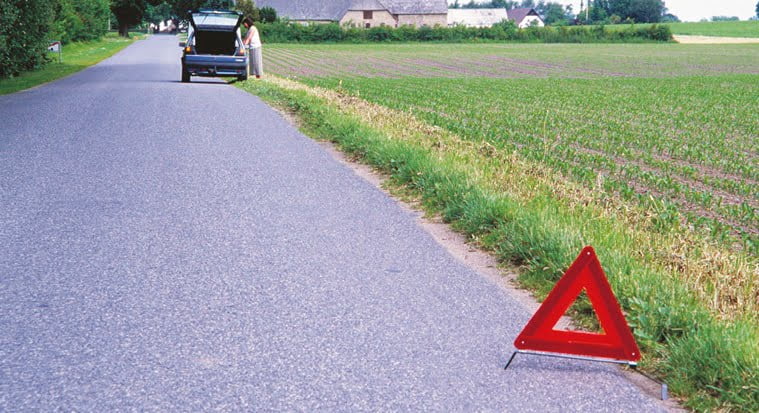
In the event of a breakdown, accident or similar in a place where stopping or parking is prohibited, you must move the car as soon as possible. On a motorway, move it completely off the carriageway if possible. If the vehicle is a danger or inconvenience to traffic, you must immediately set up the warning triangle at least 50 metres in front of the vehicle on ordinary roads and at least 100 metres in front of the vehicle on motorways. The vehicle's hazard warning lights must be used in addition to the warning triangle.
Engine failure and towing
- In the event of unexpected congestion or other immediate danger on motorways and roads outside densely populated areas, hazard warning lights may (on motorways must) be used to warn other road users. The use of hazard warning lights in other cases is prohibited.
- In the event of engine failure or similar at a railway crossing or other level crossing with tracks, you must do your best to warn the driver of the danger.
- It is legal to tow a wrecked car, tractor or motorised equipment if it is done with a solid rope, pole connection or similar and the distance between the vehicles is no more than 4 m. If the distance is more than 2 m, the rope must be clearly marked. The vehicle being towed must be driven by a person who has a driving licence for the vehicle. Do not drive faster than 30 km/h.
- Towing is prohibited if the brakes or steering of the towed vehicle are not in legal condition. In this case, you must entrust the towing to an authorised tow truck or similar
- Towing on motorways and expressways must be carried out by an authorised company.
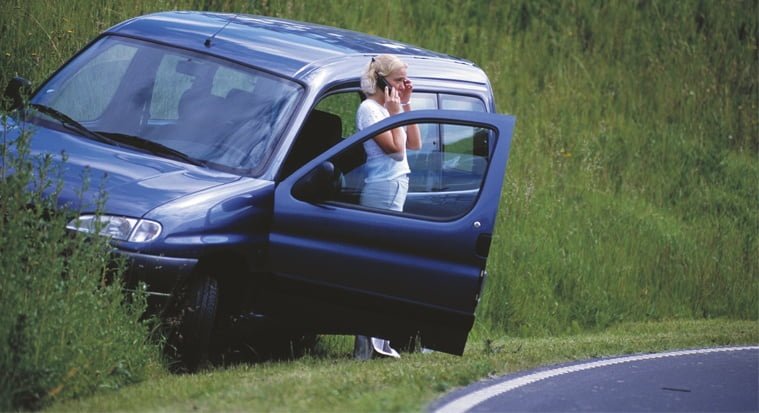
If you're near the scene of an accident, check the injuries and condition of the injured. Help as best you can at the scene. When you call the emergency centre, they need to know where you are calling from, where the accident happened and if there are any special hazards, such as fire hazards, trapped people or dangerous goods. You'll also need to know how many casualties there are and if they are in mortal danger, such as without breathing, without a heartbeat or if they have severe haemorrhaging.
Road traffic accident
You can help prevent an accident from happening. Mark the scene of the accident so that other road users do not hit the vehicles, injured people, bystanders and others at the scene. If necessary, traffic should be stopped or diverted. Remove crashed vehicles that are a hazard to traffic.
Switch off the engine of vehicles involved in accidents and do not use open flames if fuel has leaked out.
Do not approach crashed vehicles where there is a risk of a dangerous goods release. Vehicles carrying dangerous goods are marked with an orange sign.
If you can't stand the sight of blood or injured people, get other road users to help.
Once you've taken a first aid course, you'll be better able to help rescue injured people or minimise the extent of the injury.
If you damage
- A traffic sign, markings on a carriageway, cycle path, signalling system or other traffic devices, you must immediately put it back in order, regardless of whether it was your fault or not. If this is not possible, report it to the police as soon as possible and do everything you can to warn other road users.
- If you are involved in a road accident, with or without fault, you must immediately stop and help the injured. If asked, give the name and address of anyone else involved in the accident; if you have caused injury to another person, report it to the police. If there are serious injuries or fatalities, do not change the conditions or remove evidence at the scene of the accident. However, vehicles must be moved if they are a danger to traffic.
- If someone else's property is damaged, the party responsible for the damage must notify the injured party or the police.
Obligation to insure
Anyone who owns or uses (has permanent access to) a motor vehicle must have liability insurance to cover any claims for damages. A car cannot be registered, i.e. get licence plates, without liability insurance.
Handing over your vehicle to others
It is prohibited to entrust the driving of a vehicle to persons who do not hold a valid driving licence for this purpose.
Test your knowledge
Cat. B - Sections 6.1 - 6.2
Select the questions you think are the right ones.