Tractor
Driving school
theory book
for tractor
Section 2
Vehicle layout and equipment, etc.
- A vehicle must be designed and maintained in such a way that it can be used without danger and inconvenience to others and without damage to the roads.
- The owner or the person (user) who has permanent access to the vehicle is responsible for ensuring that the vehicle is in a legal condition.
- The driver of a vehicle must at all times ensure that the vehicle and any trailer are in a safe condition, in particular that the steering, braking, signalling and signalling devices and lights are working properly and that the coupling to any trailer is in order.
Vehicle checks
The police can stop a vehicle and have it inspected for faults and defects and check that the driver fulfils the conditions for legally driving the vehicle.
Tractor layout and equipment
A tractor must be equipped with:
- Steering wheel
- Brakeman
- Headlights
- Signalling device
- Indicator lights
- Stop light
- Equipment to ensure driver orientation
- Air rubber rings
- Connection device
- Reverse gear
- Rear reflective devices
- Signage for slow-moving vehicles, "tractor triangle"
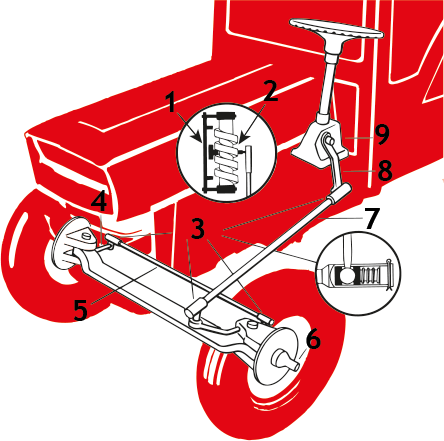
Steering wheel
A tractor must be equipped with a steering device that allows the tractor to be steered easily, safely and quickly.
By easy is meant:
- That you can turn the steering wheel from one extreme position to the other with one hand while driving slowly. No uneven resistance should be felt and no squeaking or scraping sounds should be heard.
By safely understood:
- That all moving parts are free from each other and that all nuts and bolts are double secured against separation.
By fast is understood:
- That the steering wheels react immediately to any steering wheel movement.
- The steering system must be designed and maintained in such a way that there is no significant play at all due to wear and tear or similar.
- A tractor's steering system may be designed so that the steering movement from the steering wheel to the turning wheels is transmitted by hydraulics (fluid pressure), and on special models the tractor may have steering on both front and rear wheels.
- Some power tools can be electrically controlled.
- For tractors with hydraulic steering, it must be possible to steer the tractor even if the motorised oil pump fails.
- A modern tractor with hydraulic steering will normally be illegal to tow on the road when the engine cannot run, as the steering will be very heavy to operate.
- A hydraulic steering unit is a complicated mechanism and the safest method for proper maintenance can be found in the tractor's owner's manual.
- A vehicle must be designed and maintained in such a way that it can be used without danger and inconvenience to others and without damage to the roads.
- The owner or the person (user) who has permanent access to the vehicle is responsible for ensuring that the vehicle is in a legal condition.
- The driver of a vehicle must at all times ensure that the vehicle and any trailer are in a safe condition, in particular that the steering, braking, signalling and signalling devices and lights are working properly and that the coupling to any trailer is in order.
Measuring rat droppings:
Steering wheel play is the amount that the steering wheel can be turned without moving the front wheels.
Wheel play is measured with the front wheels in the straight-ahead position and on tractors with hydraulic steering, the engine must be running.
1) Turn the steering wheel to the left until the front wheels just move.
2) Hold a finger still next to a steering wheel spoke or other measuring point on the steering wheel.
3) Then turn the steering wheel to the right until the front wheels move again.
4) The wheel play can then be measured as the distance between your finger and the measuring point. The permissible wheel play depends on the size of the steering wheel and the construction of the steering system and can be between 0 and 5 cm.
On a modern tractor with hydraulic steering, significant wheel play is not acceptable.
Brakeman
A tractor must be equipped with a service brake, parking brake and emergency brake.
The service brake must be able to brake the tractor safely, quickly and effectively at all speeds and load conditions, and the braking distance must not exceed 11.5 metres at 30 km/h.
The parking brake must be able to remain in the applied position.
The emergency brake (which can be the handbrake or one circuit of a dual-circuit braking system) must be able to safely stop the tractor if the service brake fails.
Drift brake are usually hydraulic, which means that the force from the brake pedal is transferred to the wheels using oil pressure.
The service brake can also be 'mechanical acting', meaning that the force from the brake pedal is transmitted to the wheels through a system of pull or push rods, rocker arms and cables.
The parking brake is always mechanical.
The tractor is usually equipped with two brake pedals. These are used when driving off-road for sharp turns.
When driving on the road, the brake pedals must always be locked together, and failure to do so will result in a "cut" in your driving licence if checked by the police.
A hydraulic brake on a modern tractor may be fitted with a brake fluid reservoir where the fluid level must be between the minimum and maximum mark. Most modern tractors receive auxiliary pressure from the tractor's hydraulic system and are supplied with fluid from this. See the tractor's owner's manual. The parking brake is usually a handbrake like on a car. It can also be designed as a simple locking device for the brake pedals, as well as a locking device in the gearbox or transmission.
The parking brake must be able to remain in the applied position.
The parking brake must be able to keep the tractor stopped on a slope with a gradient of 12%, i.e. with a 12 cm drop per 100 cm horizontal length.
Safe is understood to mean:
- That the tractor's brake tracks are of equal length, that hose and pipe connections are not bruised and leaking, that the brake pedals are securely mounted and have a sufficiently grooved surface so that the foot cannot slip during braking.
- That the pedals have a suitable clearance of approx. 1-4 cm to prevent the brakes from dragging while driving and thus becoming ineffective.
Fast is understood to mean:
- That the brake pedals must not be depressed more than 2/3 of the way down individually. There they should feel hard, not springy and floppy, and they should not sink downwards with sustained pressure.
Sufficiently effective means:
- That the tractor must be able to brake within 11.5 metres at a speed of 30 km/h. If the parking brake is a handbrake, it must be able to remain applied. To check this, pull it up and test whether the application mechanism can withstand a blow, for example with a clenched fist. Full braking performance must be achieved before the handbrake lever reaches its top position.
The tractor may sometimes be equipped with compressed air brakes that require special maintenance. You can find information about this in the tractor's owner's manual.
Stopping distance, Reaction distance and Braking distance.
A stopping distance is the distance the tractor travels from where the driver perceives an obstacle to where the tractor stops.
The stopping distance can be divided into two other lengths, called the reaction distance and the braking distance.
The reaction distance is the distance the tractor travels from the point where the driver perceives an obstacle to the point where braking begins.
The braking distance is the distance the tractor travels from the point where braking begins to the point where the tractor stops.
The reaction time will usually be around 1 second.
Reaction time is prolonged by fatigue, illness, lack of sleep, alcohol, various medications, euphoriant substances and special mental states such as depression, rage or even binge drinking. These conditions should not be an issue for the responsible tractor driver.
During normal attentive driving, you should expect to be able to perceive and react in about 1 second.
If, on the other hand, you concentrate on driving and have the imagination to anticipate dangerous situations, you can begin to avert danger by putting your foot on the brake pedal (emergency position).
This gives you a shorter reaction time and allows you to quickly apply the brakes if the situation actually develops as you anticipated.
When you have been driving a tractor for a while, you will have gained some good experience, which can be called "risk knowledge", and one of the purposes of this book and the driving lessons is to give you good risk knowledge before you roll out into traffic on your own.
10 km/h corresponds to approximately 3 metres per second
20 km/h corresponds to approximately 6 metres per second
30 km/h (full tractor speed) equates to approximately 9 metres per second.
The reaction length with a 1 second reaction time would be approximately 9 metres.
The maximum braking distance for a tractor is 11.5 metres at 30 km/h, but under normal circumstances it will be shorter.
Speed and braking distance
As speed increases, braking distance increases dramatically. This simply means that if you double the speed, the braking distance will be 4 times as long, and if you increase the speed 3 times, the braking distance will be 9 times as long.
- Here the tractor is travelling at 10 km/h. Brake hard and measure the brake length, e.g. 1 metre.
- Here the tractor is travelling 20 km/h, i.e. twice as fast, and braking hard. The braking distance will now be 2 x 2 = 4 times longer = 4 metres.
- Here the tractor is travelling again, this time at 30 km/h, i.e. 3 times as fast. Brake hard again and the braking distance will now be 3 x 3 = 9, i.e. 9 times longer. As you can see, you can be fooled if you sit in the tractor and think you can "stop on the spot".
Electrical systems, lights, etc.
A tractor must be equipped with an accumulator so that mandatory position lights, tail lights, licence plate lights and marker lights can be kept switched on without the engine running.
Fuses or other equivalent protection must be fitted in the electrical system to prevent the risk of fire in the tractor due to a short circuit in the electrical system.
Lights and reflective devices
Tractors must be equipped with the following:
- Two dipped-beam headlamps with white or amber light that can illuminate the road at least 30 metres in front of the tractor without dazzling.
- Two position lights with white light and two rear lights with red light, all clearly visible at a distance of at least 300 metres without dazzling. (Position lights that are combined with amber dipped beam may also be amber).
- Licence plate light so that the rear licence plate can be read from a distance of at least 20 m (only on registered tractors).
- Two rear-facing red reflectors that must not be triangular.
- Special marking as a slow-moving vehicle "tractor triangle"
The following vehicles must be fitted at the rear with a red fluorescent ("self-illuminating") triangle ("tractor triangle") with a red reflective edge:
- Tractor
- Power tool,
Indicator lights
Tractors must be equipped with indicators, two in front, two on the side and two at the rear.
The indicator light must be amber in colour and clearly visible in sunlight. Must flash at an appropriate frequency (speed).
The indicator light must be connected to the indicator lamp or audible signal. Faults are detected if the indicator light does not switch on, is constantly lit or if its flashing speed changes significantly.
In addition, the turn signal must be designed as a hazard warning signal, i.e. all turn signal lights flash simultaneously.
Stop lights.
A tractor must be equipped with two stop lamps that show a strong red light to the rear and that switch on immediately when the service brake is applied.
On a modern 4-wheel drive tractor, the 4-wheel drive will often be activated electrically when braking so that it brakes on all 4 wheels and the 4-wheel drive indicator light will illuminate.
Permitted lights
Tractors may be fitted with two additional dipped-beam headlamps (which may not be switched on at the same time as the mandatory dipped-beam headlamps), four main-beam headlamps, two front fog lamps, one or two working lamps, one searchlight, one or two rear fog lamps, one or two reversing lamps and, subject to certain width and length requirements, parking lamps and end-outline marker lamps.
Signalling device (horn).
Tractors must be equipped with a clear sounding horn with a constant tone.
Yellow signalling lights (rotor flash).
An amber marker light is a light with a flashing amber light that is visible on all sides.
When a vehicle is marked with yellow flashing lights, it is to warn other traffic of a vehicle that, due to its size, low speed or position on the road, must be passed with caution.
Traffic lights
A tractor must be marked with one or more yellow marker lights when work tools and protruding equipment are attached that protrude more than 15 cm from the side of the tractor or are wider than 2.55 metres. The lights must be used while driving and when stopping or parking on the carriageway.
View.
A tractor must be designed in such a way that the driver's seat provides the necessary direct forward and lateral visibility. If the cab is fitted with windows, the windscreen must be made of toughened or laminated glass. The other panes, including any small panes in the front wall of the cab at floor level, must be made of toughened or laminated glass or shatterproof plastic material.
- Tractors with a windscreen must be equipped with a windscreen wiper.
- A tractor must be equipped with an exterior rear-view mirror on the left side. In addition, a tractor must be equipped with an exterior rear-view mirror on the right side when a work tool or trailer is attached that obstructs the driver's direct view to the rear. The rear-view mirrors must be adjusted so that the driver has the necessary view to the rear.
Remember to adjust the mirrors before driving.
- defective/incorrectly adjusted mirrors are the cause of many accidents.
Driver protection (cab or roll bar).
All wheeled tractors with at least two axles and an unladen weight of at least 500 kg, as well as tracked tractors, must be equipped with an approved roll-over protection cab or guardrail. Roll-over protective structures must be approved by the labour inspectorate.
Cantilevered parts.
Protruding parts, including implements mounted on the tractor, must not endanger other road users.
Shielding of gripping claws.
Tractors with gripping claws on the wheels must be equipped with a guard to prevent the protruding parts from grabbing road users.
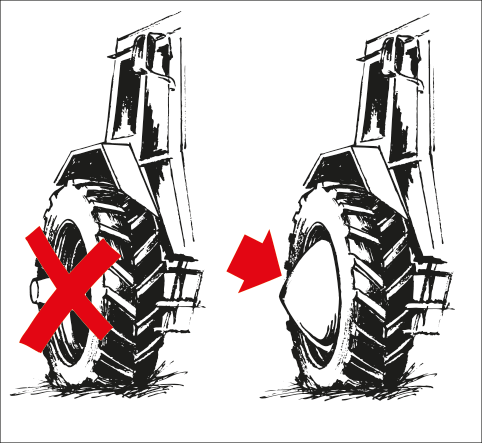
Axle end shielding
If the axle ends of the rear wheels of the tractor protrude, or if the rear wheels of the tractor can be adjusted so that the axle ends protrude, the tractor must be fitted with a suitable shielding device, e.g. as follows
- Flat, smooth wheel capsule that covers the axle ends and seals tightly to the wheel disc, or
- Sloped guard in front of the rear wheels made of sheet metal that extends beyond the protruding axle ends, or
- Front bumper on the front of the tractor of the same width as the axle ends and painted white on the outer 25 cm.
Transport box.
For transport purposes, depending on the tractor's registration, a specially designed transport box can be used if:
1) The guaranteed maximum authorised weight of the tractor with full load and the maximum axle load is not exceeded.
2) The pressure on the steered wheels does not fall below 20% of the tractor's actual gross vehicle weight.
Test your knowledge
Cat. TM - Section 2
Vælg det eller de svarmuligheder som du mener er de rigtige.